Energy Markets Update
In this newsletter we cover the factors you need to know impacting US energy markets as well as news about localized utility spending, Connecticut electric rate increases, New England natural gas resiliency, and California’s plan to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Table of Contents
- Gas & Power Update
- MA LNG Terminal Gets a Lifeline
- US Utilities Ramp Up Spending
- Connecticut Electric Rate Increases
- MN Utility Proposes Dynamic Rate Structure
- California’s Clean Energy Plan Takes Shape
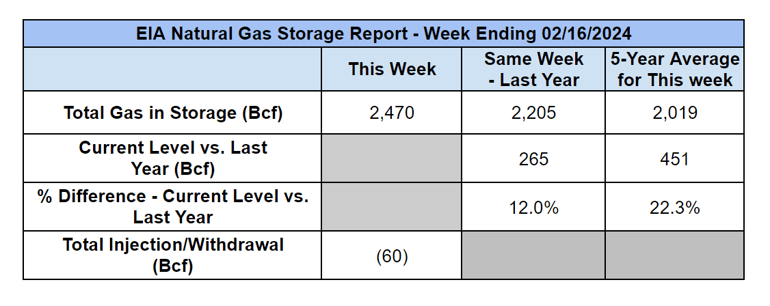
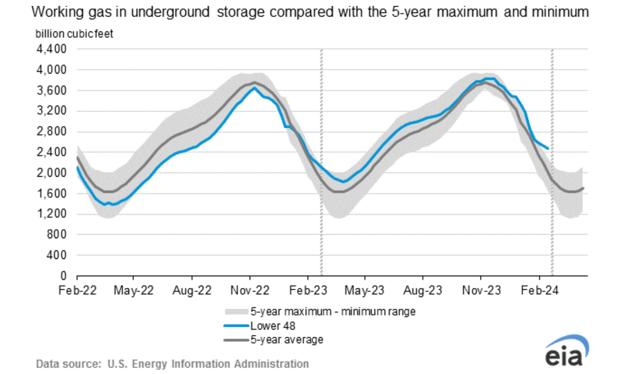
Weekly Natural Gas Inventories
The US Energy Information Administration reported last week:
- 60 Bcf decrease in US natural gas storage
- 163.3 Bcf the five-year average withdrawal for February
- 2,470 Bcf total US natural gas storage last week
- 12.0% higher than last year
- 22.3% higher than the five-year average
US Energy Market Update
A summary of recent changes and important information about the US energy markets.
- NYMEX gas rallied yesterday on the news that one of the country’s big 10 gas producers, Chesapeake Energy, will be cutting spending this year.
- On a morning earnings call, Chesapeake Energy’s CEO said it would cut spending by 20% in 2024, that the market “doesn’t need our gas” right now, and that it would both hold back supply and drill wills but not complete them.
- Chesapeake, which is a major producer in the Hayneville and Marcellus shale regions and produces about 3-4% of the nation’s gas, also said it expects demand to grow in 2025. In other words, it is still preparing for expansion next year but plans to average about 2.7 Bcf/d in 2024 vs 3.4 Bcf/d in 2023. This would remove about 250 Bcf from the market.
- The news lifted prices for the prompt 8 month strip (Mar-Oct) by 12%, the largest daily move in years. Prices were back down 2-5% today after a soft storage report from the Energy Information Administration.
NYMEX Monthly Gas Contract Pricing For March 2024 - November 2025 on February 20th and 21st
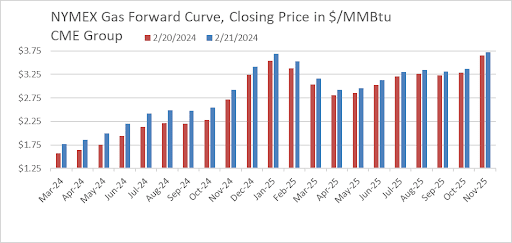
Source: CME Group
- This is unquestionably a significant market response, however the context is important. Prices were at multi-year lows ahead of the news. The March contract closed at $1.58 per MMBtu on Tuesday after weeks of unabated freefall. Even with the 20-30 cent daily rally, gas for the remainder of 2024 is still priced below $2.40 per MMBtu.
- Production also remains strong at over 105 Bcf/d, the last couple of storage reports have been bearish (i.e. lower withdrawals), and a warm front is taking hold across most load pockets in the coming weeks.
The NOAA US Temperature Outlook for February 29 - March 6
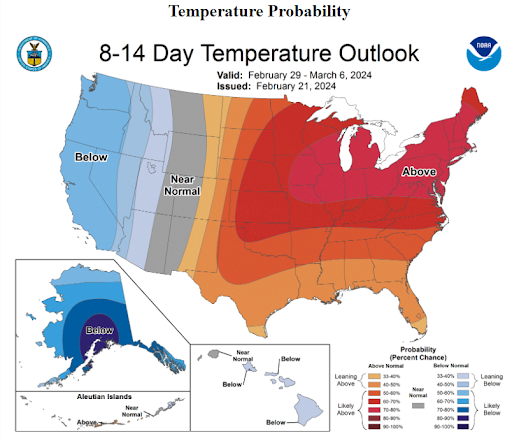
Sources: NOAA
- Nonetheless, this should be taken as a clear sign that the market may have found a bottom in the near term. It also seems likely that buyers will be hastened into the market, not wanting to miss out on bargain basement hedging opportunities for the remainder of the year. This could generally be price supportive in the near term.
- Oil prices continued to move up early in the new year on tighter fundamentals and growing weariness of the geopolitical environment – continuing attacks by the Houthis from Yemen, widespread Iranian aggression by proxy, a bolder Russian posturing that seems more inclined to sow chaos and uncertainty.
- Brent crude is trading around $83/bbl, up about 8% this month. US light crude (WTI) is trading around $78.
- In response to the Biden Administration's pause on new LNG export terminal approvals, the Republican-controlled House of Representatives passed a bill to strip the Administration of its oversight powers and give FERC more autonomy over the process. The bill would need to clear the Senate and a signature from Biden, both of which are unlikely. It is unclear whether the Administration’s move is merely a pause or the beginning of a pivot. LNG exports represent about 13% of daily domestic production and are expected to reach 20% in the next few years.
- The US Energy Information Agency expects generation capacity power plants to slow in 2024, to the lowest rate in 16 years. Approximately 5.2 GW of capacity is expected to come offline, an approximately equal mix of coal and gas, but this is down from 13.5 GW in 2023.
MA LNG Terminal Gets a Lifeline
The important Everett, Massachusetts liquified natural gas (LNG) terminal has struck a deal with the local gas utilities Eversource Energy and National Grid. Without these deals, it is likely that the terminal would have shut down, which would have put a strain on the Massachusetts natural gas infrastructure.
- In a significant breakthrough for the energy security and grid stability of the Northeast, Constellation’s Everett LNG import terminal has reached agreements with Eversource Energy and National Grid, likely preventing the terminal from closure. The two gas utilities now await the Massachusetts Department of Public Utilities' approval.
- As mentioned in last week’s newsletter, the terminal's biggest customer, Constellation-owned Mystic River 8 and 9 Power Plant, is set to close in May 2024. Without sufficient contracts to replace Mystic Plant's retirement, the terminal is in danger of closure, and the Northeast could face supply shortfalls during weather events and times of grid stress.
- New England has the unfortunate distinction of having to rely on LNG imports at times–the only market in the US that actually imports LNG–and the future of the terminal has been putting grid planners on edge for years.
- Last week National Grid’s Boston Subsidiary, Boston Gas Co., and Eversource Energy both reached six-year agreements for imported LNG and storage facilities at the terminal.
- Aside from assessing regional infrastructure and demand needs, the Massachusetts DPU will now assess how the terminal’s service extension until 2030 would align with regulators' goal to decrease the region’s natural gas delivery and consumption, a competing regulatory objective of the state. Additionally, the DPU will assess impacts on residential consumers, as National Grid noted that their contract with the Everett Terminal could increase residential bills by $3.50 during winter months.
- This is a small price to pay if it can help to keep both power and gas prices more stable in the region, which most agree that it will. It’s important to remember that the wholesale power market in New England is roughly 30-40% larger than the gas market over the winter, but it is primarily driven by wholesale spot gas prices.
- Most analysts believe that the two utilities extension is the most viable alternative to meeting capacity constraints, as other supply options, like pipeline expansion projects, are still underway in the Northeast and require significant construction time and regulatory approval processes.
Utilities Plan to Increase Spending; Are Customer Rate Increases on the Horizon?
A number of utilities around the US have increased their capital spending plans at the beginning of 2024. The increases are largely due to greater investments in clean energy, transmission upgrades, and grid resiliency.- Portland, Oregon’s utility, Portland General Electric Co. (PGE), added more than $1.4 billion of projected costs to their capital expenditure between 2024-2028. This raises the total capital spend projection for this time frame to greater than $6 billion.
- PGE added an additional $1.2 billion to its projected capital expenditures between now and the end of 2027. This increase includes transmission and grid modernization improvements amongst others.
- PGE’s spend for 2028 has also increased due to a $250 million award to the Confederated Tribes of the Warm Springs Reservation from the federal government to more than double the capacity of the Bethel-Round Butte transmission line to 500 kV.
- PGE’s President and CEO Maria Pope said these improvements will help meet customer growth, bring more clean energy to customers, and help improve the grid in the region.
- In early February 2024, PGE put out an RFP for renewable generation and energy storage for its grid. The utility estimates that it will need between 3,500 MW and 4,500 MW of renewables to meet its 80% greenhouse gas reduction goal by 2030 and subsequent 100% goal by 2040.
- PGE added an additional $1.2 billion to its projected capital expenditures between now and the end of 2027. This increase includes transmission and grid modernization improvements amongst others.
- PPL Corp., which owns utilities in Pennsylvania, Kentucky, Virginia, and Rhode Island, is planning to invest more than $14 billion in its companies over the next four years. This funding is intended to make upgrades and improvements to address clean energy integration.
- On February 16, PPL updated their spending forecast for 2024-2027 to $14.3 billion of capital investment, a $2.4 billion increase over its forecast for 2023-2026.
- The company’s Executive Vice President and CFO Joseph Bergstein Jr. expects most of that funding to affect Pennsylvania and Kentucky to make needed transmission and reliability upgrades and improvements for both gas and electric utilities.
- The Kentucky Public Service Commission (PSC) partially approved the energy investment plan submitted by PPL’s Kentucky utilities in November 2023. This included 1,000 MW of new solar and energy storage capacity to replace retiring fossil fuel generation. The utilities were ordered to keep operating about 900 MW of coal-fired generation to maintain reliability in the area. A new 621 MW combined cycle plant was approved, but a second was denied due to a lack of current need.
- PPL’s President and CEO Vincent Sorgi expressed concern about meeting the energy needs of the future. He quoted an industry projected increase of 200% to 300% in electricity demand and a difficulty to meet that demand in a cost effective way without further investment in renewables and clean gas-fired generation.
- PPL also noted that they had seen an increase in data centers in their Pennsylvania and Kentucky territories with the potential for continued demand growth from these large energy users.
- On February 16, PPL updated their spending forecast for 2024-2027 to $14.3 billion of capital investment, a $2.4 billion increase over its forecast for 2023-2026.
- Southern Co., which has utilities in Alabama, Georgia, Illinois, Mississippi, Tennessee, and Virginia, has increased its five-year capital spending plan by $5 billion.
- The company expects electricity sales to grow 2% for 2024-2025 and increase to 6% annually from 2025-2028. One of their utilities, Georgia Power Co., expects retail electric sales to grow 9% over the same time period.
- Southern Co’s Executive Vice President and CFO Daniel Tucker expressed that sales growth, especially from manufacturing facilities and data centers, could actually decrease customer rates. Tucker also mentioned that the past four years have seen an increase of about 200,000 residential customers, which is the largest increase in a four-year period in the company’s history.
- Southern Co’s capital plan for 2024-2028 totals about $48 billion, $38.7 billion of which is earmarked for its regulated utilities. This funding is focused on increasing the clean energy production, transmission, and resiliency of the grid. This budget is 12% greater than the projection in 2023.
- The company expects electricity sales to grow 2% for 2024-2025 and increase to 6% annually from 2025-2028. One of their utilities, Georgia Power Co., expects retail electric sales to grow 9% over the same time period.
- Consolidated Edison Inc. (ConEd), who serves customers in New York City and Westchester County, New York, increased its capital investment plan for 2024-2025 by about $283 million. This funding is earmarked for projects that will strengthen grid resiliency and prepare it for the clean energy transition.
- This updated capital plan raises the total investment for 2024-2025 to about $10 billion, which is increased from the $9.8 billion projection made last year. From 2026-2028 ConEd plans to invest an additional $18 billion of funding.
- ConEd’s Senior Vice President and CFO Robert Hoglund mentioned that ConEd has a number of “significant infrastructure projects” planned to help meet the ever evolving needs of the modern electric grid.
- This updated capital plan raises the total investment for 2024-2025 to about $10 billion, which is increased from the $9.8 billion projection made last year. From 2026-2028 ConEd plans to invest an additional $18 billion of funding.
- Rate Impacts. As a counterpoint to capital spending increases, Exelon Corporation said it would decrease spending by $1.25B in ComEd (Illinois) due to an unfavorable ruling in its most recent rate case. The commission in Illinois authorized an 8.91% return on equity (ROE) for ComEd, a substantial discount from the 9.28% recommended by an independent judge, and the utility's requested 10.50%. Some of the aforementioned spending increases have been formally proposed for cost recovery. Others will, in good time. Customers in affected areas can reach out to their account representative at Veolia for more specific information on impacts and timing.
Connecticut Increases Rates Due to Contract with Millstone Nuclear Plant
Connecticut electric utilities Eversource Energy and United Illuminating Company have proposed significant rate increases.
- In Connecticut last week, Eversource Energy and United Illuminating Company, an Avangrid subsidiary, filed a significant rate increase request with Connecticut’s Public Utilities Regulatory Authority (PURA).
- Eversource’s request entailed a $38 increase, or 19%, for residential customers, while United Illuminating filed for a $30, or 12.3%, increase for residential customers. In total, Eversource’s rate increase aggregates to $784 million. Commercial and industrial customers of United Illuminating Company on the utility’s general service rate, could experience bill increases upwards of 11%. Both these requests would begin starting May 1st, 2024 if approved.
- United Illuminated representatives stated that 87% of the rate increase was due to contracts the utility has with the Millstone and Seabrook nuclear power plants and low-income electric programs the utility offers. The state rescued its last beleaguered nuclear plant, Millstone, in 2019 by entering into a 10-year PPA at approximately $50 per MWh. This contract looked ingenious in 2022 when prices surpassed $100 per MWh, but the deal is now underwater with LMPs averaging $25-40 in recent months.
- Eversource cited unpaid customer balances stemming from COVID-19 and PURA’s shift in rate case methodology. In 2020, the authority shifted the methodology from being able to incorporate future costs into rate adjustment analyses to only using the previous year’s actual revenues and costs.
- State legislators criticized the two utilities, highlighting the utilities’ recent capital expenditures and promising company valuation metrics, while simultaneously claiming to require more capital and payments from overdue customers.
Xcel Energy’s Proposal for Variable Residential Rates in Minnesota
Xcel Energy, an electric utility in Minnesota, has proposed switching residential customers to variable rates to ease grid strain during times of high demand.
- Although this topic relates to residential customers and less so to our readers, we thought it was a notable incidence of a utility thinking outside the status quo.
- California utilities have long led the way on time of use (TOU) rates for both commercial and residential customers, and many other utilities have piloted them in recent years. We anticipate that this will be a growing trend as we see increasing cost volatility throughout the day due in part to intermittent renewable energy generation. Who knows, possibly this is the start of a trend. Either way, it’s worth keeping an eye on.
- Xcel Energy has proposed switching Minnesota residential electric customers to variable rates, with peak rates being seven times more expensive from 3-8 p.m. on weekdays and nearly twice as expensive as all other hours (See visual provided by Xcel below).
Xcel Energy Minnesota’s Proposed Electric Rate Structure Represented Visually
 Source: Xcel
Source: Xcel
- The potential shift is aimed at easing pressure on the electric grid during high-demand periods, something we discussed utilities around the country grappling with in January. Doing so would optimize the use of wind power generated at night, and give customers more control over their power bill.
Xcel Energy's Proposed New Rate Structure - Residential
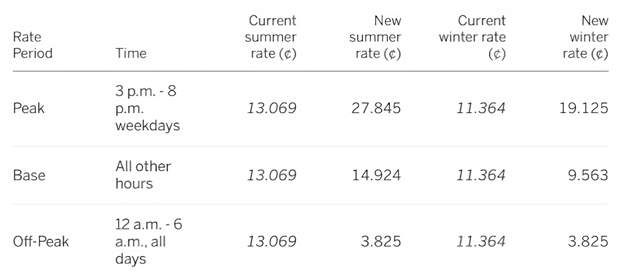
Source: Star Tribune
- Xcel is already implementing time-of-use rates in the Twin Cities Colorado, with promising results from a test run where the average customer saved a small amount of money.
- Some experts believe however that Xcel's rate design, with a significant gap between peak rates and off-hours, may be an outlier nationally and could lead to backlash. Indeed, off-peak power is priced at a significant discount, so there is good incentive to run the dishwasher overnight. In our view, why have TOU rates at all if there is no material difference between the periods?
- If approved, the rates would be implemented in mid-to-late 2025 after the completion of a rollout of new energy meters, and customers would have the option to opt out of variable rates for the current flat rate if they choose.
California’s Clean Energy Plan Takes Shape
The California Public Utilities Commission recently approved a greenhouse gas emissions reduction plan that will have a large impact on the California grid moving forward.
- On February 15th, the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) approved a comprehensive greenhouse gas emission reduction plan, including several changes to its renewable generation targets and electricity portfolio standards. These targets will have significant impacts on cost and price formation for years to come, however advanced guidance on resource adequacy goals provides large market participants with options and inputs on how to plan for the future.
- The CPUC set a 25 million metric ton (MMT) greenhouse target for the electric sector by 2035 and mandated that approximately 56 GW of clean energy generation be added to the grid by then.
- The CPUC’s decision also included a “preferred” electricity portfolio that consists of 19 GW of solar, 18.5 GW of lithium-ion batteries, and 4.5 GW of offshore wind, all to be added by 2035. The CPUC’s detailed resource breakdown is provided below. The plan provides for some flexibility in resource allocations based on many unknowns, but deviations must be documented.
The Planned and Selected Capacity for the CPUC’s Greenhouse Gas Reduction Target
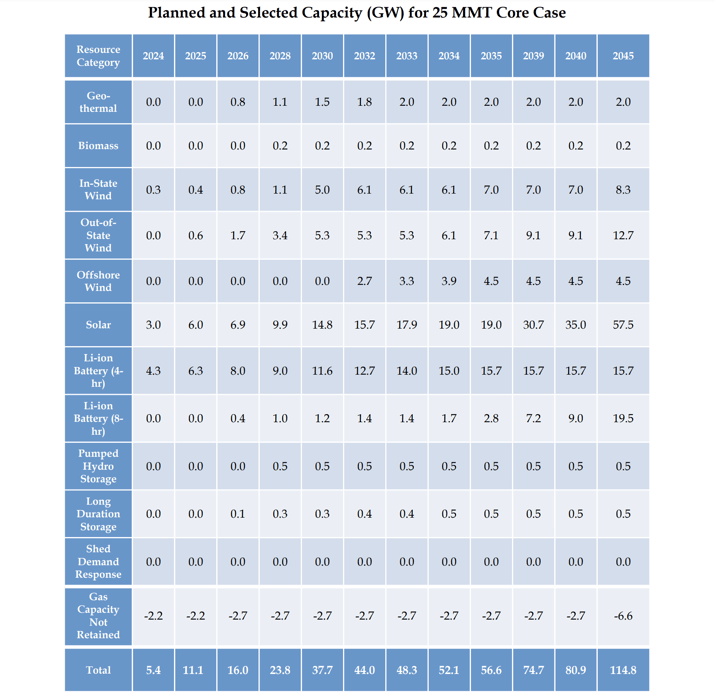 Source: CPUC
Source: CPUC
- If successfully instated, the CPUC’s plans will reduce electric sector emissions by 28 MMT, a 58% reduction compared to CAISO's 2020 emission levels. This plan is further expected to reduce emissions by 85 percent and achieve 113% clean energy by 2045.
The Planned and Selected Near and Medium-Term Capacity for California’s Grid From the CPUC
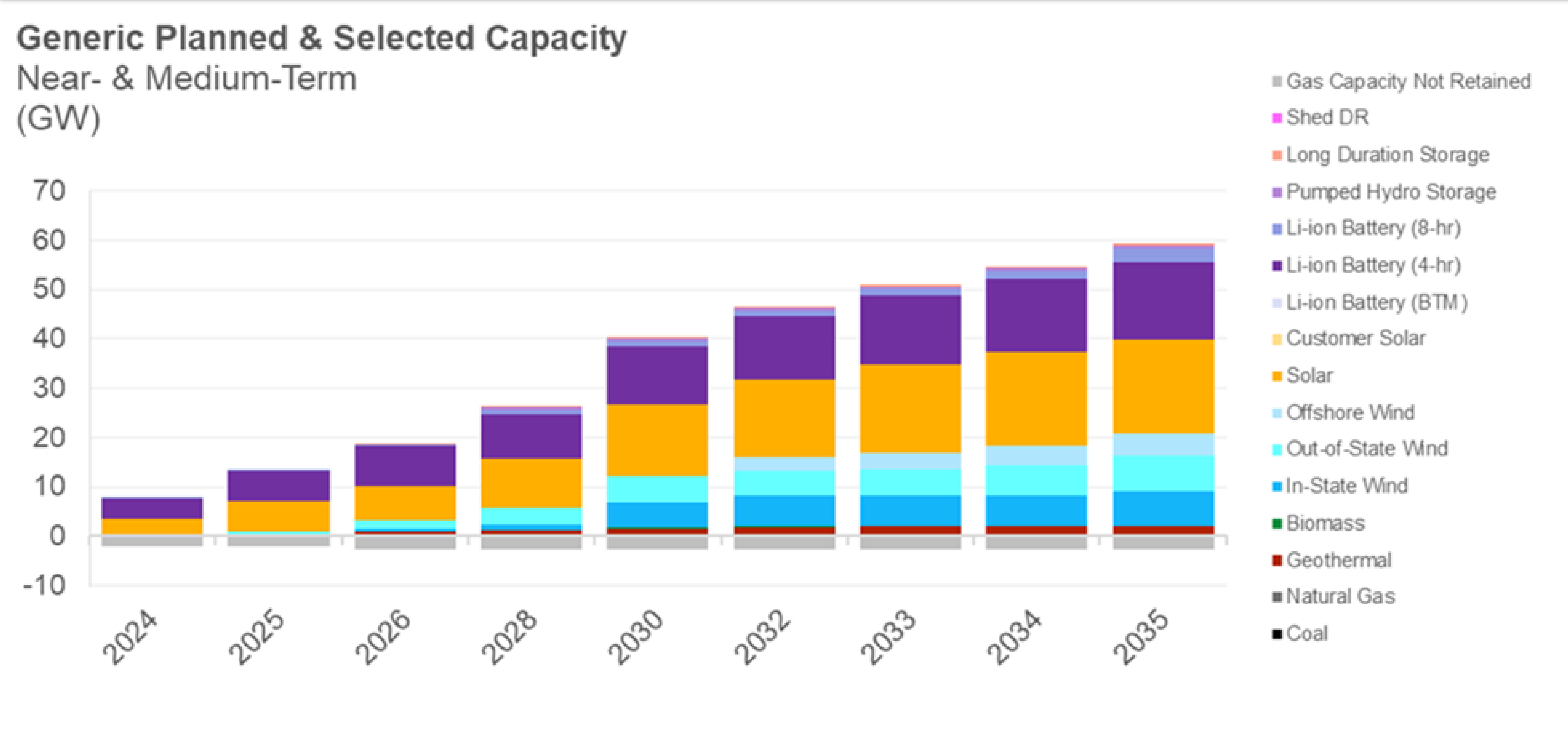
- The use of natural gas-fired power plants connected to the California ISO transmission system would also decrease by roughly 70% from 2024 to 2035, according to a PUC commissioner.
- One of the big “unknowns” is the future of the Diablo Canyon nuclear facility. The 2,240 MW clean energy facility’s license will expire in 202 and 2025, the PUC is asking utilities to come up with a portfolio of replacement options, the utilities say they need more time, and both the Governor and the Federal Government are seeking to extend the plant’s license.
- CPUC’s decision referenced Senate Bill 100 (also known as “The 100 Percent Clean Energy Act of 2018”), which set a target of 100 percent clean energy for the state by 2045. The commission believes this additional ruling was needed to ensure the bill’s targets were met.
- Another notable component of CUPC’s decision highlights recent regulators' strides to lower natural gas consumption and dependence. The commission requested for CAISO to further analyze the transmission needed for a grid stress case where 15 GW of natural gas generation are retired by 2039.
Natural Gas Storage Data
Source: EIA
Source: EIA
Market Data
Market data disclaimer: Data provided in the "Market Data" section is for the newsletter recipient only, and should not be shared with outside parties.



