In the Beginning - Pyramids
The 1976 Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) promoted regulations around the safe and proper management of newly defined hazardous waste. As the regulations evolved, a waste hierarchy model emerged that summarized what the regulations were trying to accomplish — moving from most preferred management methods to those least preferred. The top of the inverted pyramid is: avoid and reduce waste followed by: reuse waste, recycle waste, recover energy, treat waste and lastly, dispose or landfill waste.
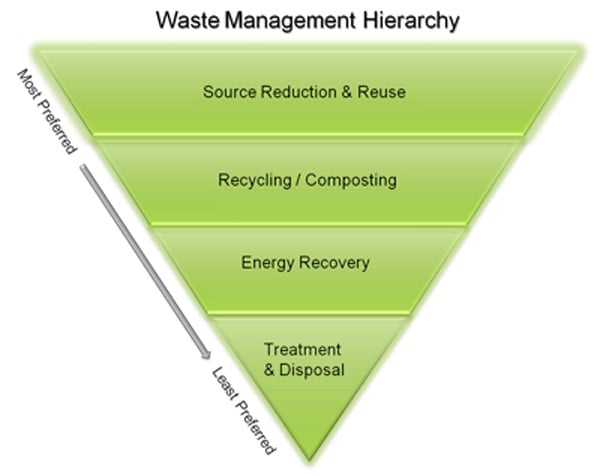
This model has kept environmental, health and safety (EHS) professionals busy in the intervening four decades. The result has been a significant reduction in waste landfilled and an increase in reuse, recycling and energy recovery. Goals met, right? Well, not exactly. We still have waste. And much greater volumes are not regulated under RCRA.
Triple Bottom Line – Venn Diagrams
Business writer John Elkington claims to have coined the phrase the “triple bottom line” in 1994. It robustly incorporates development that is economically, environmentally and socially acceptable where the three circles intercept In the last several years, environmentalists have adopted it as a lens to view sustainability efforts by all stakeholders. Along the way EHS practitioners have become EHS&S (second "S" for sustainability professionals).
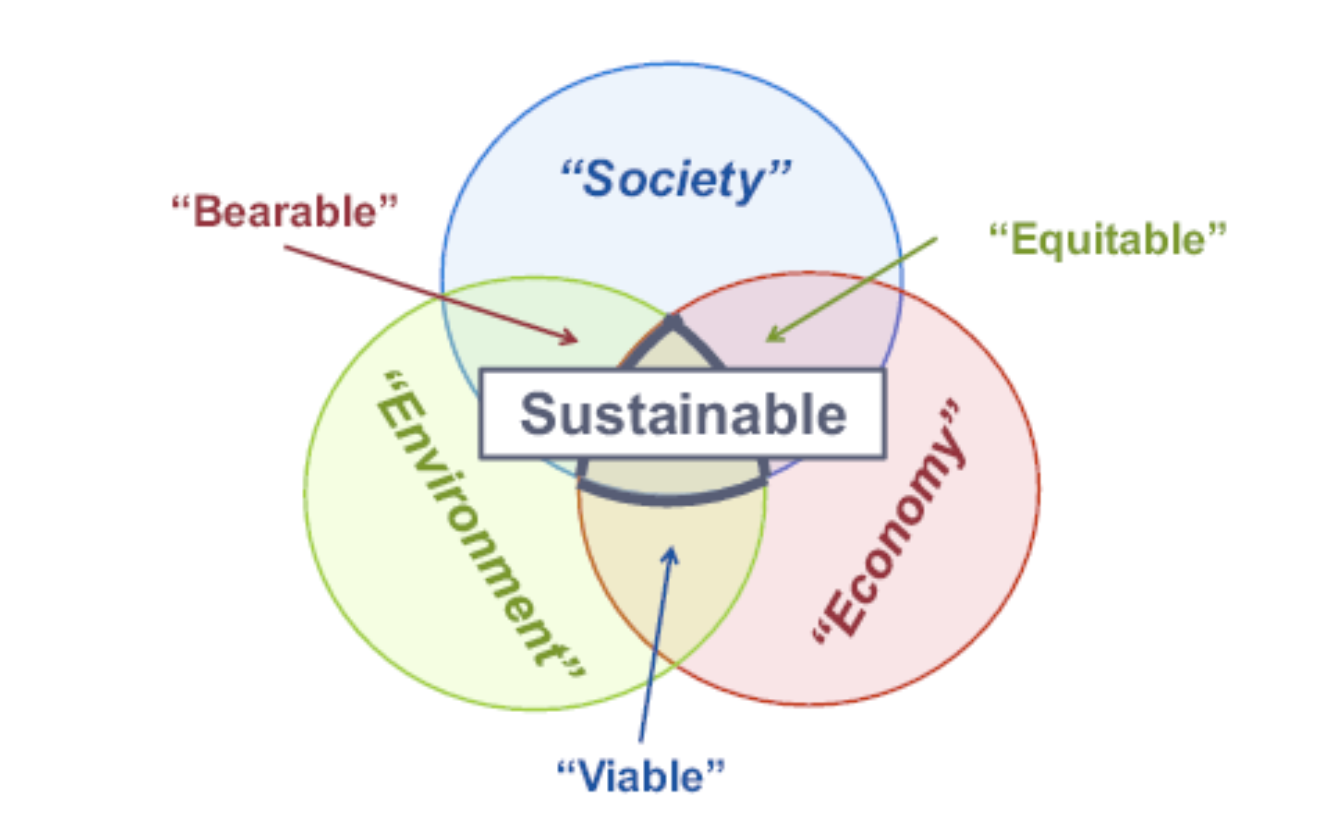
In the waste world, this meant a renewed focus on reuse, recycle and energy recovery. While there have been successes as new technologies emerged to address these management areas, much of that low-hanging fruit had been harvested. On their own or pressured by activist investors, companies began to produce annual reports on their sustainability goals. Early goals focused on waste, then included energy and water goals as metrics took shape. Greenhouse gas gained prominence as a contributor to climate change resulting in reduction targets in ESG/CSR documents.
The sustainability conversation also began to incorporate non-regulated, or solid waste. Certain commodities have always had value and been recycled: glass, cardboard, ferrous and non-ferrous metals and paper for example. These materials, if contaminated, and other materials often end up in a landfill.
To make progress on these ever-expanding goals, the conversation began to migrate outside EHS&S circles to include design, manufacturing, supply chain and other areas of the enterprise. If waste could be designed out, if material could be segregated on the plant floor, if another supplier could use the material as a raw input to their process, sustainability would be achieved. Right? Yes, but, there is more to be done.
Thinking Circular – The Can Do Loop
According to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, German chemist Michael Braungart is credited with coining the term cradle to cradle in the late 1970’s. Today, many environmentalists credit Braungart’s work as forming the basis for today’s circular economy (CE) concept. The circular economy is a holistic approach to viewing an economic system.
Where sustainability had its origin in material recovery, recycling and reuse, circularity aims to eliminate wastes of all kinds; material, capacity, life cycle and value. This circle model still addresses wasted materials as before, but also seeks to address the wasted capacity,. Think about the percent of time you actually drive your car, for example, to wasted life cycles due to planned obsolescence or non-upgradeable products, to lastly the wasted value of materials that cannot be recovered at the end of a product’s life.
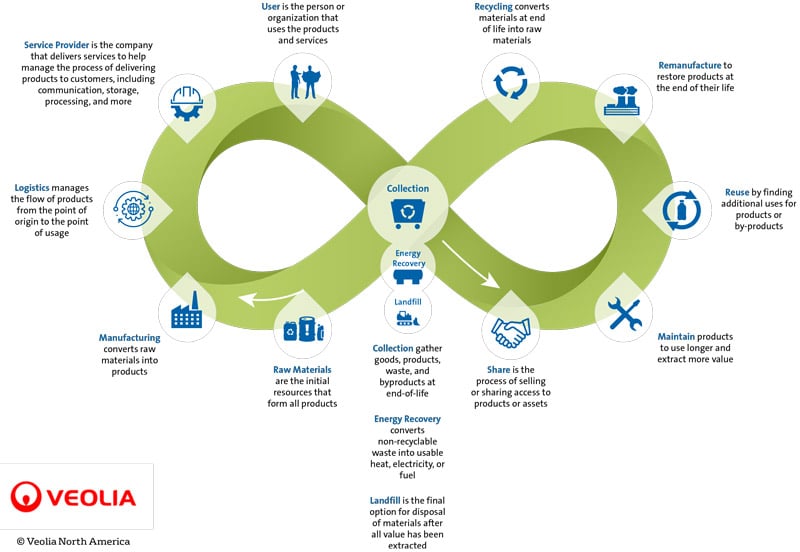
Today’s EHS&S business programs include a wide variety of responsibilities, many of which support CE efforts, though primarily focused on wasted materials.
Activities include:
- Auditing: internal and external
- Reporting: ESG, safety and compliance performance, Right to Know and BRS
- Compliance and risk management: programs, processes and tools
- Training: company, state and federal requirements
- Safety: programs, processes and tools
- Permitting: air, water and waste issues and requirements
- Waste or material management issues: storage, auditing facilities, ESG/CSR goal performance, preparing, manifesting, shipping and tracking waste
Sustainability/CE issues:
- Support the organization’s S/CE goals related to waste/material management with zero waste or zero waste to landfill
- Integrate with the business to support circularity in design, raw material selection, manufacturing processes, use by customer and post-use
- Address water issues such as treatment and reduced use
- Address energy issues such as reduced use, increased efficient, and resiliency
Clearly waste and byproducts will be part of mankind’s existence. Our challenge will be to address this opportunity with renewed focus on old and new models as we move closer to circularity.



