Energy Markets Update
Weekly natural gas inventories
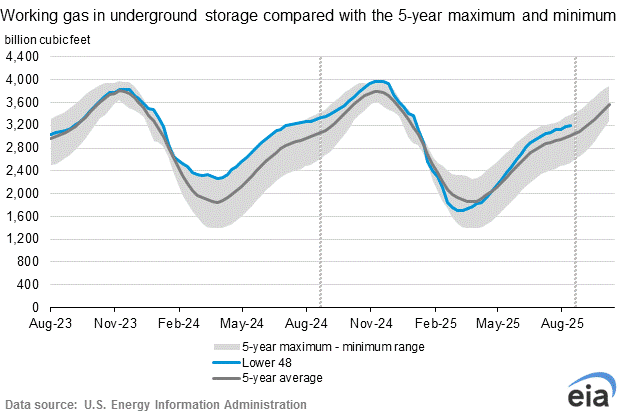
The U.S. Energy Information Administration reported last week that natural gas in storage increased by 16 Bcf. There was an injection for the same week last year of 86 Bcf while the five-year average injection is 87 Bcf. Total U.S. natural gas in storage stood at 2,427 Bcf last week, 15.7% less than last year and 4.9% lower than the five-year average for this time of year.
Joint federal & state task force created to aid transmission development
On June 17, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) and the National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners (NARUC) announced a new task force armed with the goal to improve electric transmission buildout across the US. The task force will be a joint federal and state body, with NARUC to nominate 10 state regulators to join the task force with all acting FERC commissioners. Among other goals, the primary aim of the task force is to identify barriers to planning and development of transmission infrastructure necessary to meet renewable policy goals, as well as identify possible solutions to those barriers.
With Biden’s accelerated decarbonization goals at the forefront of the nation’s energy policy, studies have found that the US can reach its net-zero emissions target by 2050, but to do so, significant investment will need to be made into the nation’s transmission system. One Princeton study found that a 60% expansion of the US electric transmission grid by 2030 and possibly a tripling of today’s transmission capacity by 2050 would be necessary to meet federal goals. Despite such goals, recent transmissions development has not met this pace, as land disputes and project cost allocation disagreements slow down development.
Transmission capacity buildout is critical to the deployment of renewable energy systems and their integration into the electric grid. It is often necessary for renewable developments of significant size to be built in areas away from existing transmission infrastructure, due to the space required for wide-scale renewables. Thus, when large solar plants or wind turbine arrays are built, additional transmission capacity is necessary to link the new developments to the rest of the grid. In the Mid-Atlantic, PJM recently open a competitive solicitation process for transmission development in order to serve the offshore wind development planned off the coast of New Jersey.
A significant amount of planning, stakeholder negotiations, and problem-solving must be overcome in order to implement new transmission, a process which is further complicated when multiple states, sometimes with different policy goals, have a stake in a project. The new task force is created to identify ways to ease the development process and empower state stakeholders with FERC jurisdiction when possible.
Other goals for the body include enabling the cooperation of states with like-minded policy goals, reviewing FERC rules and regulations for transmission cost allocation, as well as identify barriers to efficient transmission development within FERC’s interconnection processes. FERC Chairman Richard Glick is also expected to announce a broader climate plan to take further action on transmission obstacles before the end of August including grid operators’ interconnection policies.
Sen. Manchin defends coal plants
At the Edison Electric Institution 2021 conference, Senator Joe Manchin of West Virginia expressed his concern regarding the Biden administration’s accelerated climate goals and defended the country’s coal-fired power plants. Manchin contended that the US has far fewer coal-fired plants compared to the 6,600 facilities operating globally and US plants have been inequitably called out by environmentalists despite the plants’ reduction of carbon emissions. The Senator’s comments come as West Virginia, the country’s leading producer of coal, is currently only producing half the amount of coal that it produced a decade ago as natural gas and renewables procure a larger share in the power plant market. Manchin also argued for increased investment and research in carbon capture and sequestration technology that would not require the extinction of reliable energy sources.
Additionally, he also expressed concern for the Biden administration’s goal for a 50-52% greenhouse gas emissions reduction across the economy by 2030, which necessitate nuclear power plants that are prospectively closing. For increased reliability, Manchin called out for tax incentives for utility companies to harden the electric grid and prevent outages from natural disasters or cyber-attacks.
While coal generation has long been a hotly contested subject that rides political lines, it is not purely green energy policy that is leading its long demise. Even before Biden’s aggressive federal goals were put forward this year, many states with little to no renewable energy requirements have seen coal plant closures induced by market forces rather than legislature. With high cost of maintenance associated with keeping plants open, and cheap natural gas becoming the predominant generation source across the nation, coal’s decline has been largely attributed to market conditions as well.
Natural Gas Storage Data

Market Data
Use the filters to sort by region
Market data disclaimer: Data provided in the "Market Data" section is for the newsletter recipient only, and should not be shared with outside parties.



